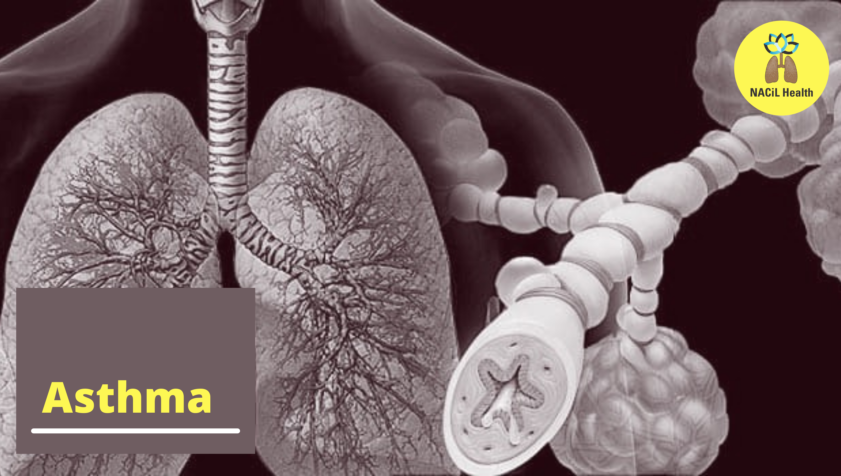
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory pathophysiologic disorder of the airways, characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchial hyper responsiveness. Asthma causes recurring periods of wheezing (a whistling sound when you breathe), coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Asthma is caused by inflammation in the tiny tubes that carry air in and out of your lungs.
Asthma affects people of all ages caused by repeated periods of wheezing (a whistling sound when you breathe), coughing, chest tightness and shortness of breath. These symptoms are caused by inflammation or narrowing of lung airways that are sensitive to certain triggers. It can be triggered by several different things such as allergies, irritants in the air like smoke or pollen, cold air or exercise
Asthma causes the muscles around the airways to tighten, which makes it harder to breathe. Asthma can also cause a sticky mucus to form inside the airways, making it even more difficult to breathe. Asthma is not contagious, and cannot be spread from person-to-person or animal-to-person.
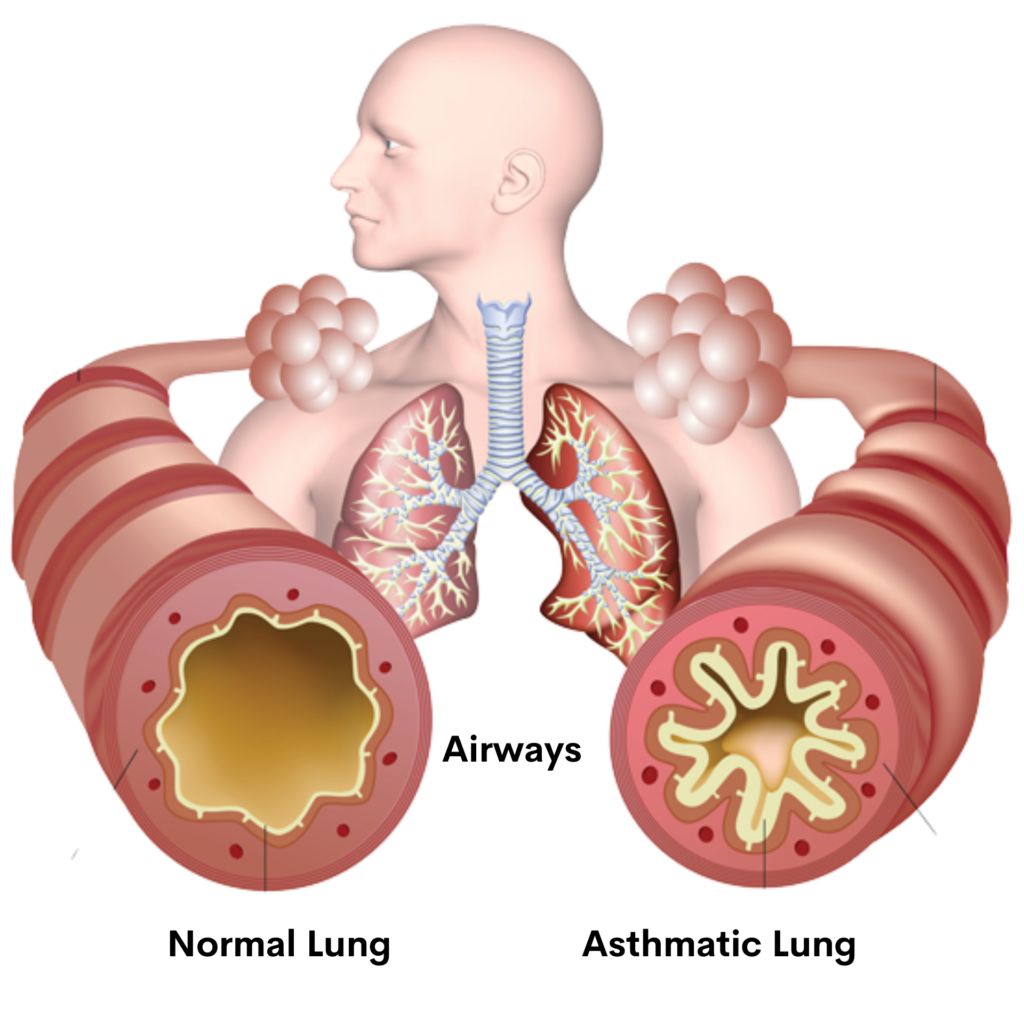
There are two main types of asthma: allergic asthma and non-allergic asthma. Most people with asthma have allergic asthma which they get from being sensitive to specific substances called Allergens. Allergens such as Pollen, Mold, dust mites, Pet dander and cockroaches. Asthma can occur at any age but it most commonly starts during childhood.
Asthma attacks are unpredictable and can vary in severity from mild to life threatening. Asthma attacks are often brought on by physical activity or cold air.
Asthma signs and symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Chest Tightness
Although asthma is a chronic obstructive condition, it is not considered as a part of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), as this term refers specifically to combinations of disease that are irreversible such as bronchiectasis and emphysema. Unlike these diseases, the airway obstruction in asthma is usually reversible; however, if left untreated, the chronic inflammation from asthma can lead the lungs to become irreversibly obstructed due to airway remodelling. In contrast to emphysema, asthma affects the bronchi, not the alveoli. The combination of asthma with a component of irreversible airways obstruction has been termed the asthma-chronic obstructive disease (COPD) overlap syndrome (ACOS). Compared to other people with “pure” asthma or COPD, people with ACOS exhibit increased morbidity, mortality and possibly more comorbidities (more than one disease or condition is present in the same person at the same time).
Asthma is a serious disease that affects the quality of life for millions of people around the world. The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified asthma as one of the top 10 causes of death among children under five years old. In 2019 asthma affected approximately 262 million people and caused approximately 461,000 deaths. Most of the deaths occurred in the developing world. Asthma often begins in childhood, and the rates have increased significantly since the 1960s.
Asthma cannot be cured completely, but it can be controlled to the point that the symptoms become negligible. As a chronic and lasting condition, asthma is not curable. It is highly treatable, though, so long as a patient has professional support. Some children with asthma will outgrow it by adulthood. But, for many, asthma is a lifelong condition. It is possible to live a healthy life despite asthma.
Many people with asthma, like those with other chronic disorders, use alternative treatments; Halotherapy can be considered as a complimentary therapy if you are going through Asthma that can help to reduce the inflammation and reduces the symptoms of Asthma to lead quality better life.